Written by: Andrew Roberts
Reviewed by: Dr. Matthew Scott, PhD & DHSc
Date: 04/10/2010
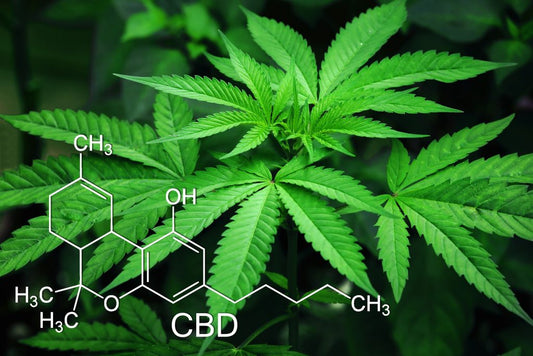
What is CBD (Cannabidiol)?
Cannabidiol, commonly called CBD, is a natural substance derived from the Cannabis plant.
What Are the Benefits of CBD?
There are countless success reports of people using CBD to treat, suppress, and or ease a variety of symptoms. Medical applications include but are not limited to: epilepsy, chronic pain, multiple sclerosis, spasms, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, nausea, convulsions, inflammation, and many other conditions, including cancer. CBD has been shown to be effective for decreasing anxiety and helping in a number of inflammation-related problems, including arthritis and other inflammatory ailments as well as multiple sclerosis.
CBD is also proven to inhibit the growth of the MRSA bacterium (a strain of staphylococcus resistant to antibiotics), which causes several difficult-to-treat infections. CBD has strong antioxidant properties. As each person is different, and because CBD’s beneficial effects are still under study, we strongly encourage you to do your own research before incorporating CBD to your daily life.
Where Does CBD Come From?
CBD is extracted and separated from specific varieties of cannabis, often as Hemp or Marijuana. Chemically, CBD is one of 85 chemical substances known as cannabinoids, which are all found in the cannabis plant. CBD is the most abundant compound in Hemp, typically representing up to 80% of its extracts. CBD is completely different from THC and CBD cannot get you “high”. It is actually impossible to get “high” by smoking or ingesting CBD-Rich hemp (that has only traces of THC), as it is also impossible to get high by consuming CBD oil products (that contain no THC at all). CBD is extracted in oil form and is often found mixed in hemp oil extracts in varying concentrations.
Is Cannabidiol Legal?
Yes, CBD is legal- depending on the plant its derived from and state laws. CBD is actually unrelated to the chemical chain that results in THC. They share some characteristics but are created via different paths. Again, unlike THC, CBD is considered a legal and is safe to consume in any amount and concentration.
WHAT IS CANNABIS?
Marijuana and Hemp come from the same genus of flowering plant: Cannabis
There are three distinct species of cannabis plant: Cannabis Sativa, Cannabis Indica, and Cannabis Ruderalis.
A little about each species of cannabis…
Cannabis Sativa is the most common strain of cannabis. It has been cultivated throughout history for countless purposes, including the production of seed oil, food, hemp fiber, medicine, and recreation to name a few.
Cannabis Ruderalis is native to Russia. Flowers earlier and is able to withstand harsher conditions than Cannabis Sativa and Cannabis Indica. Although it’s a hardier species of the three, it is relatively poor in terms of cannabinoids. Ruderalis has a lower THC content than Sativa or Indica.
Cannabis Indica was discovered in India. It is shorter and bushier than sativa.
Cannabis cultivation for thousands of years have led to several different types of cannabis even within the same species, depending on the purpose the cannabis was cultivated for.
Hemp vs Marijuana: What’s the Difference?
The defying change from Cannabis hemp to Cannabis marijuana is at the plant level. Simply put, Cannabis is Cannabis. The compounds that make the plant cannabis have to be the same, otherwise it’s not Cannabis. The only difference is the varying amount of THC in the plant (dry weight). If the cannabis plant contains less than .3% THC (dry weight) it is hemp, if the THC % exceeds .3% its marijuana. It’s honestly that simple.
Marijuana-producing cannabis characteristics: short, bushy, and have high amounts of THC. Marijuana is typically bred with one purpose: maximizing THC concentration. Hemp always has trace amounts of THC and naturally occurring high amounts of CBD, in fact it has the highest CBD/THC ratio of all cannabis strains.
Meaning hemp’s chemical profile makes it incapable of inducing intoxicating effects.
Since hemp is naturally rich in CBD and has been bred to have only trace amounts of THC, many people today are turning to hemp products as an alternative to medical marijuana. Medical marijuana is not legal in all states in the US and many countries worldwide, while products made from hemp can be a safe and legal alternative. You can get many of the same beneficial effects of medical marijuana from hemp products without getting “high.”
Medical Marijuana CBD Oil vs Hemp CBD Oil?
The answer: Cannabidiol is Cannabidiol
Here’s the main concept to understand. In regards to its chemical composition, CBD remains unchanged regardless of which plant produces it. There is no room for different interpretations and the substance is just that. Any single difference in the molecular composition would mean it’s no longer CBD (Cannabidiol) but another substance entirely. The main difference between the two remains that CBD oil from medical marijuana can contain any varying amount of THC. As a result, this type of CBD oil is considered a Schedule I drug and is not legal in many states in the US and countries worldwide. As hemp is naturally high in CBD and contains only traces of THC, the hemp oil produced from it is safe and non-psychotropic. This CBD oil is actually a lot different than the oil produced by extracting the fatty acids of the cannabis plants that are bred for medicinal purposes. Besides the difference in THC concentration, the CBD oils will also have differing amounts of other cannabinoids. But those make up a much smaller percentage of the overall volume and are not as pronounced in their effects as CBD or THC are. So, if you are looking for a safe and legal CBD product, Our CBD oil produced from hemp is a great choice, because it’s naturally rich in CBD and has almost no THC.
Cannabidiol Oil
We’ve established the fact that naturally occurring CBD is the same CBD regardless of the plant it came from. However, CBD and CBD oil are not in fact the same thing. As we’ve seen above, CBD is a chemical compound with sharply defined characteristics, while CBD oil is a mixture of various natural substances as they are derived from the plant of cannabis. The production of hemp oil involves extracting the fatty acids from the cannabis plant. Within these fatty acids fat-soluble substances can be found, and as cannabinoids are fat-soluble, they come out of the plant, dissolved in the oil.
To make this more concrete, let’s use an example here. This is a high-CBD hemp oil product made from hemp. It has a concentration of CBD between 18% and 24%. This means that it has 18%–24% parts CBD dissolved in the actual oil, which is composed by other substances. So 18%–24% is pure CBD, and the rest are hemp oil extracts and other fatty acid substances.
CBD vs THC:
Cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) are the two most abundant cannabinoids found in cannabis. CBD and THC interact with specific cells, causing a number of different effects in our bodies. CBD and THC have a wide range of applications and are similar at the molecular level, however the chemical properties of CBD and THC vary widely enough to classify THC as a psychotropic drug strictly controlled by federal authorities, while CBD is regarded as legal and safe worldwide. CBD is considered to have wider applications than THC. Since CBD has been much less studied than THC, scientists assume that there are many new applications of CBD that haven’t yet been discovered.
How CBD Works!
Cannabinoid: Naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant. There are dozens of compounds including Cannabidiol (CBD), THC, and a host of other cannabinoids. Together they are responsible for the benefits and drawbacks to medical marijuana and hemp-based products. CBD and its sister cannabinoid compounds are classified as phytocannabinoids, meaning that it’s derived from plants.
There are also several other types of cannabinoids:
Endocannabinoids: Cannabinoids produced within the body’s endocannabinoid system.
Synthetic Cannabinoids: manufactured via chemical reactions in laboratories.
Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabinoid receptor sites: Sites on the body specifically made for cannabinoids.
These sites make up the endocannabinoid system: responsible for numerous physiological and mental processes that occur naturally within the body, such as appetite, pain sensation, mood, memory, and more. These receptors fall into two types: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are found mainly in the brain (but also in the liver, kidneys, and lungs), while CB2 receptors are found mainly in the immune system. Cannabinoid substances actually bind with these receptors to coordinate various functions across the body.
Effects Cannabinoids Have on the Body?
Some of these cannabinoids interact strongly with one or both CB receptors, causing various effects, from regulating mood and helping us concentrate, to causing euphoric effects and feeling “high” (like THC). Other cannabinoids, like CBD, have fewer direct effects on the endocannabinoid system.
External vs. Internal Cannabinoids
The endocannabinoid system works mainly with our body’s own cannabinoids, which are produced internally. However, when cannabinoids are taken externally, it’s difficult to distinguish between the clinically desirable effects and the therapeutically undesirable effects of various phytocannabinoids. This is because cannabinoid receptors send a variety of signals that often interconnect to coordinate the body’s functions, so it’s hard to tell them apart.
Example: CB1 receptors send signals that simultaneously regulate pain and reduce inflammation, while cannabinoids that interact with CB2 receptors can at the same time affect gastrointestinal inflammatory response and peripheral nervous system sensitivity.
Some cannabinoids interact synergistically, producing unique effects that are not found when using them individually.
Example: CBD inhibits THC’s psychotropic effects when the two are taken together. However, CBD does this (and produces many other effects) without directly interacting with the cannabinoid receptors. Cannabidiol has a particularly low potential for binding with the CB1 and CB2 receptors, instead it acts as an antagonist of the receptors’ agonists. All this mean is, CBD keeps the receptors working at optimal capacity and helps the function of all other cannabinoids, including the body’s own endocannabinoids.
CBD Effects:
- Agonists – chemicals that bind to a receptor and activate it to produce a biological response.
- Inverse agonists – chemicals that bind to the same receptor as agonists but produce the exact opposite result.
- Antagonists – the complete opposite of agonists as they inhibit or dampen the functions of a receptor.
The indirect interactions of CBD with the endocannabinoid system has many effects. Some of CBD’s functions include:
- Effectively increases CB1 density, amplifying the effects of all cannabinoids that bind to CB1 receptors.
- Acts as a 5-HT1a receptor agonist in the brain, a property that is largely responsible for CBD’s antidepressant, anxiolytic, and neuroprotective effects. This means that CBD has the same effects as some potent analgesics, but without the side effects.
- Acts as inverse agonist of CB2 receptors, effectively reducing the effects of cannabinoids that make CB2 receptors less responsive.
- Acts as an antagonist for the putative GPR55 receptor.
- Various modulating pharmacological effects such as modulating the function of delta opioid receptors, helping with pain, and controlling seizures.
We Conclude
Contrary to how most cannabinoids function, CBD interacts very mildly with the cannabinoid receptors themselves and instead either helps other cannabinoids to be better absorbed or stops the effects of whatever makes the receptors work less effectively. The endocannabinoid system is closely interconnected with the nervous and immune system. CBD has been shown to boost every function of our cannabinoid receptors, it may be proven to have far-reaching positive effects and could potentially be used to treat numerous neurological or immune diseases.
Cannabidiol Definitions
-
Cannabis – A type of flowering plant that includes three distinct variations: Cannabis ruderalis, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis sativa. Cannabis has a wide range of industrial and medical applications. It has been used since antiquity for its sturdy fiber, for oils, and for medicinal purposes. However, it has also been used as a recreational drug, a fact that renders the cultivation of cannabis strictly regulated because of some variations including high concentrations of THC.
-
Hemp – Hemp refers to the high-growing varieties of cannabis that are grown to be specifically bred THC under .3%.
-
Cannabinoids – A very diverse chemical family that includes natural as well as artificially created substances. Different cannabinoids have widely varied effects, with some cannabinoids proven to have medically beneficial effects and others classified as illegal drugs.
-
CBD – A naturally occurring cannabinoid, and the second most abundant constituent of the Cannabis plant. CBD is legal and safe to consume.
-
THC – The most abundant constituent of the cannabis marijuana plant and a strong psychoactive cannabinoid, THC is responsible for getting “high”, as a result, its production and usage are strictly regulated.
-
Psychoactive – Any chemical substance that can enter the brain from the bloodstream and directly affect the central nervous system is considered psychoactive. Many psychoactive substances have medical applications (such as anesthetics, psychiatric drugs, etc.), but some of these substances are used solely for recreation, causing dangerous side effects and addiction.
-
Intoxicating – Any substance that can cause you to lose control of your faculties and alter your behavior is considered intoxicating. Almost all illegal drugs have intoxicating properties, although worldwide most intoxication cases are attributed to alcohol. Intoxication can be caused by substances that directly affect the brain (i.e., psychoactive) or by indirectly causing damage to your organism (i.e., through toxicity, hence the term).